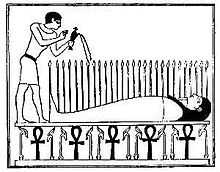
The djed is an ancient Egyptian symbol for stability which features prominently in Egyptian art and architecture throughout the country's history. `Stability' should be understood to mean not only a firm footing but immutability and permanence. The symbol is a column with a broad base which narrows as it rises to a capital and is crossed by four parallel lines. The column and the lines are sometimes brightly painted and other times monochrome. The djed first appears in the Predynastic Period in Egypt (c. 6000-3150 BCE) and continues through the Ptolemaic Dynasty (323-30 BCE), the last dynasty to rule Egypt before it became a province of the Roman Empire.
The djed is often overlooked in Egyptian art, and especially in architecture, simply because it is so ubiquitous; the djed is featured on pillars, tomb walls, architraves (the main beam which rests on pillars), palace walls, sheets of painted papyrus, and especially sarcophagi. Once one is aware of the djed and its importance to ancient Egyptian culture it is impossible to miss. It is a potent symbol associated with the god Osiris and his return from the dead. The symbol has been interpreted to represent different objects such as the god Osiris' backbone, the tamarisk tree which enclosed the god, four pillars rising one behind another, and a fertility pole raised at festivals. `Stability', however, seems to have been its prime meaning and the one which the ancient Egyptians attached the greatest importance to.
MEANING & ORIGINS
The precise origin of the djed is unknown but it was associated with the god Ptah, an early creator god in the Predynastic Period whose attributes were later assumed by the deities Atum and Osiris. According to historian Clare Gibson, the djed was an early phonogram which could also act as a pictogram or ideogram. A phonogram is a symbol representing a sound and a pictogram a symbol for a specific word or phrase while an ideogram is a symbol of a thing itself without reference to words or sounds (such as numerals where one recognizes the symbol 10 as representing a certain quantity). The djed symbolized the spoken word-concept for stability, was the written word for stability, and stood for the concept itself.
THE DJED SYMBOLIZED THE SPOKEN WORD-CONCEPT FOR STABILITY, WAS THE WRITTEN WORD FOR STABILITY, AND STOOD FOR THE CONCEPT ITSELF.
In the Predynastic Period it may have originally been a representation of a fertility pole upon which sheaves of grain were suspended at festivals. This pole may have been a feature of early fertility rituals which eventually came to be associated with the god who made the land fertile. The god Ptah carried a sceptre which combined the djed and the Ankh (symbol of life) and is referenced as "The Noble Djed" in ancient inscriptions. The Djed Pillar Festival was held annually at which an actual djed pillar was built and raised by the local priesthood on the first day of the harvest season. Raising the pillar may have originally symbolized the grains rising from the earth but, in time, came to represent the god Osiris returning from the dead.
With the rise of the cult of Osiris, the djed came to be firmly associated with him and, especially, with the tree of Byblos which enclosed him and the pillar made from that tree. The djed also symbolized the backbone of Osiris in that, just as Osiris rose from the dead, the deceased would rise from their body after death. In the same way that the human backbone allowed one to sit up and stand and walk, the spiritual image of Osiris' backbone would encourage the soul to rise up from the body and move toward the afterlife. The myth of Osiris was one of the most popular in ancient Egypt, especially in the period of the New Kingdom (1570-1069 BCE). The story details the death of the god, his resurrection by his wife Isis, and descent to the underworld to reign as Lord of the Dead.
THE MYTH OF OSIRIS
In the beginning of time, shortly after creation, the gods Osiris, Isis, Set, Nepthys, and Horus were born of the union between Geb (earth) and Nut (sky). Osiris, as the eldest, was given reign of the earth and took his sister Isis as his wife and queen. Set grew jealous of Osiris' success and trapped him in a coffin which he then threw into the Nile River. The coffin floated to the Phoenician city of Byblos where it became lodged in a tamarisk tree by the shore. The tree quickly grew around and enclosed the coffin within it. The king and queen of Byblos noticed the tree and that it gave forth a sweet scent and so had it cut down and brought to their palace to decorate the court as a central pillar.
Isis, in the meantime, had gone searching for her missing husband and finally arrived at the court of Byblos. Disguised as an older woman, she ingratiated herself to the royal family by teaching the handmaidens how to plait their hair and became nursemaid to the young princes. Isis was particularly fond of the younger child, Dictys, and tried to make him immortal by burning away his mortal part in a flame. When the queen found her doing this one night she became upset and Isis threw off her disguise to reveal herself as a goddess. The royal couple begged her mercy for their affrontery and promised her anything she wanted; Isis claimed the tree which held her husband.
She freed Osiris' body from the tree and brought him back to Egypt to revive him but, while she was out gathering the necessary herbs, Set found the body, cut it into pieces, and scattered it across the land. When Isis found her husband had been dismembered she instantly set about collecting his remains with the help of her sister Nepthys. They found all his body parts, except for his penis which had been eaten by a fish, and he was brought back to life. Isis transformed herself into a kite and summoned the seed from Osiris' body by flying around him, drawing the seed into herself and becoming pregnant with a son, Horus. Osiris, since he was not complete, could no longer rule the living and descended to the underworld as Lord of the Dead. Horus grew to maturity and then challenged Set for rule, defeating him and restoring order to the land. The myth illustrated the importance of ma'at(harmony) and the triumph of order over chaos.
Hieroglyphic usage
The djed hieroglyph was a pillar-like symbol that represented stability. It was also sometimes used to represent Osiris himself, often combined "with a pair of eyes between the crossbars and holding the crook and flail."The djed hieroglyph is often found together with the tyet (also known as Isis knot) hieroglyph, which is translated as life or welfare. The djed and the tiet used together may depict the duality of life. The tyet hieroglyph may have become associated with Isis because of its frequent pairing with the djed.
Ceremonial usage
The djed pillar was an important part of the ceremony called 'raising the djed,' which was a part of the celebrations of Heb Sed, the Egyptian pharaoh's jubilee celebrations. The act of raising the djed has been explained as representing Osiris's triumph over Set. Ceremonies in Memphis are described where the pharaoh, with the help of the priests, raised a wooden djed column using ropes. The ceremony took place during the period when fields were sown and the year's agricultural season would begin corresponding to the month of Choiak, the fourth month of the inundation season called akhet. This ceremony was a part of one of the more popular holidays and celebrations of the time, a larger festival dedicated to Osiris conducted from the 13th to 30th day of the Choiak month. Celebrated as it was at that time of the year when the soil and climate were most suitable for agriculture, the festival and its ceremonies can be seen as an appeal to Osiris, who was the God of vegetation, to favor the growth of the seeds sown, paralleling his own resurrection and renewal after his murder by Seth.
Further celebrations surrounding the raising of the djed are described in a relief in Amenhotep III's Luxor Temple. In the tomb in the temple, the scene shows the raising of the djed pillar taking place in the morning of Amenhotep III's third Heb-Sed, which took place in his thirty-seventh regnal year. The scene is described by Sigrid Hodel-Hoenes:
The anthropomorphized pillar stands at the middle left, in a shrine. It has taken the shape of a human body with the djed-pillar as its head; the eyes are udjat-eyes. The hands hold the crook and flail, the usual insignia of Osiris, the god of the dead. On its head is the tall feather crown with the solar disk. The pillar is on a high base reminiscent of the platforms visible today in many temples, on which the cult barks once stood. In front of and behind it are lotus and papyrus blossoms. Beneath the large slab of the base are two tall offering stands – one bears a libation vessel, while flowers have been laid on the other. To the right is the king himself, presenting a generously laid table. Fowl, cucumbers, blossoms, breads, and heads and ribs of beef are all lying on the upper mat, while a cow and an antelope can be seen on the lower one. Beneath these mats are four tall vessels containing unguents and oil, with bundles of lettuce sticking out among them. The vulture goddess, Wadjyt, the Mistress of the Per-nu shrine, has spread her protective wings above the sovereign, with the blue crown on his head.
— Sigrid Hodel-Hoenes, Life and death in ancient Egypt : scenes from private tombs in new kingdom Thebes, p. 222
There is also a scene depicted in the tomb to the right of the above scene which has not been well preserved. Hodel-Hoenes explains that it once showed the pharaoh, accompanied by his queen, using a rope to raise the djed pillar. Three men, probably priests of the temple of Memphis, help him in the process. A fourth priest was seen supporting the pillar. Various offerings were presented before the pillar below the ropes. Both the pharaoh and his queen are each accompanied by four pairs of young women resembling those of the sed-festival. Each of these women is rattling a Hathor sistrum, a musical instrument for percussion with a U-shaped handle and frame seen as resembling the face and horns of the cow goddess Hathor, while holding a menat, a protective amulet associated with Hathor, in the other hand. A line of hieroglyphs running just above the girls' heads in each row of women says, "Children of the king praising (or charming) the noble djed pillar." Hodel-Hoenes interprets this as identifying the girls as the daughters of Amenhotep III.
There are three additional reliefs below these two reliefs. They depict further ceremonies that accompany the erection of the djed pillar, especially games and dances. In one, food-bearers carrying edibles weave between men dancing with heavy steps. A line of singers on the far left seems to sing a short hymn to Ptah, the text of which is written alongside the line. Singing and dancing girls can be seen in the next relief, though Hodel-Hoenes comments on their seeming lack of grace, saying, "only the raised hands and the foot swinging in the air hint at the movements of a dance." The relief also depicts men involved in a boxing match and a cane dance, sports and dances which can still be seen in Egypt today.
The festival of the raising of the djed also involved re-enactments conducted at Denderah, Edfu, Busiris, Memphis, and Philae. But the most elaborate and grand celebration occurred at Abydos, the cult center of Osiris. From around the end of the third millennium BC during the beginning of the Twelfth Dynasty and perhaps as early as the Sixth Dynasty three hundred years earlier, re-enactments of the myth of Osiris and Isis – the deception and murder of Osiris by Seth, the search for Osiris by Isis and Osiris' mummification, funeral and his resurrection were performed. From the late fourth century BC, a recitation of the Lamentations of Isis and Nephthys, a poem describing Isis and Nephthys' search for Osiris, was added to the ceremony on the 25th day of the Choiak month. At the Osiris Temple in Abydos, these re-enactments are described as involving hundreds of priests and priestesses in the roles of the gods and goddesses, with 34 papyrus boats carrying the gods, a sculpture of Osiris inside an elaborate chest, 365 ornamental lamps, incense, and dozens of djed amulets.
Usage as amulets
The djed pillar was often used as amulets for the living and the dead. It was placed as an amulet near the spines of mummified bodies, which was supposed to ensure the resurrection of the dead, allowing the deceased to live eternally. The Egyptian Book of the Dead lists a spell which when spoken over a gold amulet hung around the mummy's neck, ensures that the mummy would regain use of its spine and be able to sit up. It was also painted onto coffins.
Parallels in other cultures
Parallels have also been drawn between the djed pillar and various items in other cultures. Sidney Smith in 1922, first suggested a parallel with the Assyrian "sacred tree" when he drew attention to the presence of the upper four bands of the djed pillar and the bands that are present in the center of the vertical portion of the tree. He also proposed a common origin between Osiris and the Assyrian god Assur with whom he said, the sacred tree might be associated. Cohen and Kangas suggest that the tree is probably associated with the Sumerian god of male fertility, Enki and that for both Osiris and Enki, an erect pole or polelike symbol stands beneath a celestial symbol. They also point out that the Assyrian king is depicted in proximity to the sacred tree, which is similar to the depiction of the pharaoh in the raising of the djed ceremony. Additionally, the sacred tree and the Assyrian winged disk, which are generally depicted separately, are combined in certain designs, similar to the djed pillar which is sometimes surmounted with a solar disk. Katherine Harper and Robert Brown also discuss a possible strong link between the djed column and the concept of kundalini in yoga.
The precise origin of the djed is unknown but it was associated with the god Ptah, an early creator god in the Predynastic Period whose attributes were later assumed by the deities Atum and Osiris. According to historian Clare Gibson, the djed was an early phonogram which could also act as a pictogram or ideogram. A phonogram is a symbol representing a sound and a pictogram a symbol for a specific word or phrase while an ideogram is a symbol of a thing itself without reference to words or sounds (such as numerals where one recognizes the symbol 10 as representing a certain quantity). The djed symbolized the spoken word-concept for stability, was the written word for stability, and stood for the concept itself.
THE DJED SYMBOLIZED THE SPOKEN WORD-CONCEPT FOR STABILITY, WAS THE WRITTEN WORD FOR STABILITY, AND STOOD FOR THE CONCEPT ITSELF.
In the Predynastic Period it may have originally been a representation of a fertility pole upon which sheaves of grain were suspended at festivals. This pole may have been a feature of early fertility rituals which eventually came to be associated with the god who made the land fertile. The god Ptah carried a sceptre which combined the djed and the Ankh (symbol of life) and is referenced as "The Noble Djed" in ancient inscriptions. The Djed Pillar Festival was held annually at which an actual djed pillar was built and raised by the local priesthood on the first day of the harvest season. Raising the pillar may have originally symbolized the grains rising from the earth but, in time, came to represent the god Osiris returning from the dead.
With the rise of the cult of Osiris, the djed came to be firmly associated with him and, especially, with the tree of Byblos which enclosed him and the pillar made from that tree. The djed also symbolized the backbone of Osiris in that, just as Osiris rose from the dead, the deceased would rise from their body after death. In the same way that the human backbone allowed one to sit up and stand and walk, the spiritual image of Osiris' backbone would encourage the soul to rise up from the body and move toward the afterlife. The myth of Osiris was one of the most popular in ancient Egypt, especially in the period of the New Kingdom (1570-1069 BCE). The story details the death of the god, his resurrection by his wife Isis, and descent to the underworld to reign as Lord of the Dead.
THE MYTH OF OSIRIS
In the beginning of time, shortly after creation, the gods Osiris, Isis, Set, Nepthys, and Horus were born of the union between Geb (earth) and Nut (sky). Osiris, as the eldest, was given reign of the earth and took his sister Isis as his wife and queen. Set grew jealous of Osiris' success and trapped him in a coffin which he then threw into the Nile River. The coffin floated to the Phoenician city of Byblos where it became lodged in a tamarisk tree by the shore. The tree quickly grew around and enclosed the coffin within it. The king and queen of Byblos noticed the tree and that it gave forth a sweet scent and so had it cut down and brought to their palace to decorate the court as a central pillar.
Isis, in the meantime, had gone searching for her missing husband and finally arrived at the court of Byblos. Disguised as an older woman, she ingratiated herself to the royal family by teaching the handmaidens how to plait their hair and became nursemaid to the young princes. Isis was particularly fond of the younger child, Dictys, and tried to make him immortal by burning away his mortal part in a flame. When the queen found her doing this one night she became upset and Isis threw off her disguise to reveal herself as a goddess. The royal couple begged her mercy for their affrontery and promised her anything she wanted; Isis claimed the tree which held her husband.
She freed Osiris' body from the tree and brought him back to Egypt to revive him but, while she was out gathering the necessary herbs, Set found the body, cut it into pieces, and scattered it across the land. When Isis found her husband had been dismembered she instantly set about collecting his remains with the help of her sister Nepthys. They found all his body parts, except for his penis which had been eaten by a fish, and he was brought back to life. Isis transformed herself into a kite and summoned the seed from Osiris' body by flying around him, drawing the seed into herself and becoming pregnant with a son, Horus. Osiris, since he was not complete, could no longer rule the living and descended to the underworld as Lord of the Dead. Horus grew to maturity and then challenged Set for rule, defeating him and restoring order to the land. The myth illustrated the importance of ma'at(harmony) and the triumph of order over chaos.
"I am He of the Djed pillar
the son of He of the Djed pillar
I was conceived in Djedu
I was born in Djedu"
Hieroglyphic usage
|
| ||
ḏd in hieroglyphs |
|---|
The djed hieroglyph was a pillar-like symbol that represented stability. It was also sometimes used to represent Osiris himself, often combined "with a pair of eyes between the crossbars and holding the crook and flail."The djed hieroglyph is often found together with the tyet (also known as Isis knot) hieroglyph, which is translated as life or welfare. The djed and the tiet used together may depict the duality of life. The tyet hieroglyph may have become associated with Isis because of its frequent pairing with the djed.
Ceremonial usage
The djed pillar was an important part of the ceremony called 'raising the djed,' which was a part of the celebrations of Heb Sed, the Egyptian pharaoh's jubilee celebrations. The act of raising the djed has been explained as representing Osiris's triumph over Set. Ceremonies in Memphis are described where the pharaoh, with the help of the priests, raised a wooden djed column using ropes. The ceremony took place during the period when fields were sown and the year's agricultural season would begin corresponding to the month of Choiak, the fourth month of the inundation season called akhet. This ceremony was a part of one of the more popular holidays and celebrations of the time, a larger festival dedicated to Osiris conducted from the 13th to 30th day of the Choiak month. Celebrated as it was at that time of the year when the soil and climate were most suitable for agriculture, the festival and its ceremonies can be seen as an appeal to Osiris, who was the God of vegetation, to favor the growth of the seeds sown, paralleling his own resurrection and renewal after his murder by Seth.
Further celebrations surrounding the raising of the djed are described in a relief in Amenhotep III's Luxor Temple. In the tomb in the temple, the scene shows the raising of the djed pillar taking place in the morning of Amenhotep III's third Heb-Sed, which took place in his thirty-seventh regnal year. The scene is described by Sigrid Hodel-Hoenes:
The anthropomorphized pillar stands at the middle left, in a shrine. It has taken the shape of a human body with the djed-pillar as its head; the eyes are udjat-eyes. The hands hold the crook and flail, the usual insignia of Osiris, the god of the dead. On its head is the tall feather crown with the solar disk. The pillar is on a high base reminiscent of the platforms visible today in many temples, on which the cult barks once stood. In front of and behind it are lotus and papyrus blossoms. Beneath the large slab of the base are two tall offering stands – one bears a libation vessel, while flowers have been laid on the other. To the right is the king himself, presenting a generously laid table. Fowl, cucumbers, blossoms, breads, and heads and ribs of beef are all lying on the upper mat, while a cow and an antelope can be seen on the lower one. Beneath these mats are four tall vessels containing unguents and oil, with bundles of lettuce sticking out among them. The vulture goddess, Wadjyt, the Mistress of the Per-nu shrine, has spread her protective wings above the sovereign, with the blue crown on his head.
— Sigrid Hodel-Hoenes, Life and death in ancient Egypt : scenes from private tombs in new kingdom Thebes, p. 222
There is also a scene depicted in the tomb to the right of the above scene which has not been well preserved. Hodel-Hoenes explains that it once showed the pharaoh, accompanied by his queen, using a rope to raise the djed pillar. Three men, probably priests of the temple of Memphis, help him in the process. A fourth priest was seen supporting the pillar. Various offerings were presented before the pillar below the ropes. Both the pharaoh and his queen are each accompanied by four pairs of young women resembling those of the sed-festival. Each of these women is rattling a Hathor sistrum, a musical instrument for percussion with a U-shaped handle and frame seen as resembling the face and horns of the cow goddess Hathor, while holding a menat, a protective amulet associated with Hathor, in the other hand. A line of hieroglyphs running just above the girls' heads in each row of women says, "Children of the king praising (or charming) the noble djed pillar." Hodel-Hoenes interprets this as identifying the girls as the daughters of Amenhotep III.
There are three additional reliefs below these two reliefs. They depict further ceremonies that accompany the erection of the djed pillar, especially games and dances. In one, food-bearers carrying edibles weave between men dancing with heavy steps. A line of singers on the far left seems to sing a short hymn to Ptah, the text of which is written alongside the line. Singing and dancing girls can be seen in the next relief, though Hodel-Hoenes comments on their seeming lack of grace, saying, "only the raised hands and the foot swinging in the air hint at the movements of a dance." The relief also depicts men involved in a boxing match and a cane dance, sports and dances which can still be seen in Egypt today.
The festival of the raising of the djed also involved re-enactments conducted at Denderah, Edfu, Busiris, Memphis, and Philae. But the most elaborate and grand celebration occurred at Abydos, the cult center of Osiris. From around the end of the third millennium BC during the beginning of the Twelfth Dynasty and perhaps as early as the Sixth Dynasty three hundred years earlier, re-enactments of the myth of Osiris and Isis – the deception and murder of Osiris by Seth, the search for Osiris by Isis and Osiris' mummification, funeral and his resurrection were performed. From the late fourth century BC, a recitation of the Lamentations of Isis and Nephthys, a poem describing Isis and Nephthys' search for Osiris, was added to the ceremony on the 25th day of the Choiak month. At the Osiris Temple in Abydos, these re-enactments are described as involving hundreds of priests and priestesses in the roles of the gods and goddesses, with 34 papyrus boats carrying the gods, a sculpture of Osiris inside an elaborate chest, 365 ornamental lamps, incense, and dozens of djed amulets.
Usage as amulets
The djed pillar was often used as amulets for the living and the dead. It was placed as an amulet near the spines of mummified bodies, which was supposed to ensure the resurrection of the dead, allowing the deceased to live eternally. The Egyptian Book of the Dead lists a spell which when spoken over a gold amulet hung around the mummy's neck, ensures that the mummy would regain use of its spine and be able to sit up. It was also painted onto coffins.
Parallels in other cultures
Parallels have also been drawn between the djed pillar and various items in other cultures. Sidney Smith in 1922, first suggested a parallel with the Assyrian "sacred tree" when he drew attention to the presence of the upper four bands of the djed pillar and the bands that are present in the center of the vertical portion of the tree. He also proposed a common origin between Osiris and the Assyrian god Assur with whom he said, the sacred tree might be associated. Cohen and Kangas suggest that the tree is probably associated with the Sumerian god of male fertility, Enki and that for both Osiris and Enki, an erect pole or polelike symbol stands beneath a celestial symbol. They also point out that the Assyrian king is depicted in proximity to the sacred tree, which is similar to the depiction of the pharaoh in the raising of the djed ceremony. Additionally, the sacred tree and the Assyrian winged disk, which are generally depicted separately, are combined in certain designs, similar to the djed pillar which is sometimes surmounted with a solar disk. Katherine Harper and Robert Brown also discuss a possible strong link between the djed column and the concept of kundalini in yoga.